low end tidal co2 during cpr
End tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 monitoring is the noninvasive measurement of exhaled CO 2 first studied clinically by Smallhout and Kalenda in the 1970s. More Than Just a Number.

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow
ETCO2 levels reflect the adequacy with which carbon dioxide CO2 is carried in the blood back to the lungs and exhaled.

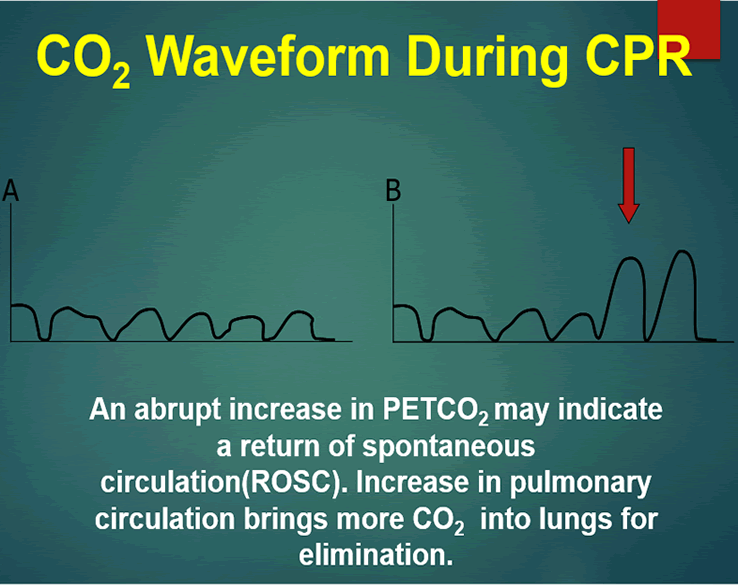
. N Engl J Med 1988318607-11. 1 that etCO 2 can distinguish massive PE from hemorrhagic shock and 2 that PE with cardiac arrest reduces etCO 2 during resuscitation to a greater extent than arrhythmic cardiac arrest. Loss of ETCO2 may be the first sign that CPR is needed.
A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 as measured by waveform capnography is considered a physiologic measure of cardiac output in low-flow states and has been proposed in the 2010 consensus resuscitation guidelines as a possible real-time metric to assess the impact of CPR quality. On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing.
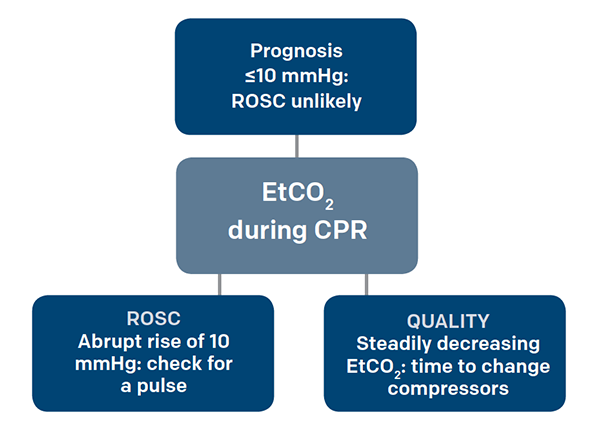
Available evidence has established that ETCO2 measurement can provide an indication of cardiac output and pulmonary blood flow24 Non. End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detection requires air movement. Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement.
Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition. In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. What should end-tidal CO2 be during CPR.
End-tidal CO2 as a guide to successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. 5 In low-flow states such as during CPR delivery of CO 2 to.
Crit Care Med 198513910-11. Cardiac output and end-tidal carbon dioxide. Here are five things you should know about waveform capnography in cardiac arrest.
End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 is the level of carbon dioxide that is released at the end of an exhaled breath. End-tidal carbon dioxide concentration during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 is a noninvasive technique which represents the partial pressure or maximal concentration of CO2 at the end of exhalation.
Falk JL Rackow EC Weil MH. 39 Treveno RP Bisera J Weil MH Rackow EC Grundler WG. We investigated the effect of massive pulmonary embolism MPE on end tidal CO 2 etCO 2 and tested two hypotheses.
Ensure proper rate approximately 100min Ensure proper depth with adequate releaserecoil of thorax 12 thorax or minimum 25 inches Persistently low EtCO. Normal value is 35-45 mmHg. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status.
Normal value is 35-45 mmHg. End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 is a noninvasive technique which represents the partial pressure or maximal concentration of CO2 at the end of exhalation.

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi
Cpr Mobile Code Stand With Capnograph Capnography

Capnography During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Current Evidence And Future Directions

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Concentration During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Nejm

The Role Of Etco2 In Termination Of Resuscitation Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram
Use End Tidal Capnography For Placing Orogastric Nasogastric Tubes And Cpr Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall